Volume 13, Issue 3 (9-2023)
J Health Saf Work 2023, 13(3): 474-495 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Kurd N, Bahrami A, Afkhami A, Ghorbani Shahna F, Assari M J, Farhadian M. A Novel Magnetized Imine-linked Covalent Organic Framework Sorbent (Fe3O4@TFPA-Bd) for Microextraction of BTEX Biomarkers in Urinary Samples. J Health Saf Work 2023; 13 (3) :474-495
URL: http://jhsw.tums.ac.ir/article-1-6874-en.html
URL: http://jhsw.tums.ac.ir/article-1-6874-en.html
Nematullah Kurd1 
 , Abdulrahman Bahrami *
, Abdulrahman Bahrami * 
 2, Abbas Afkhami3
2, Abbas Afkhami3 
 , Farshid Ghorbani Shahna4
, Farshid Ghorbani Shahna4 
 , Mohammad Javad Assari4
, Mohammad Javad Assari4 
 , Maryam Farhadian5
, Maryam Farhadian5 


 , Abdulrahman Bahrami *
, Abdulrahman Bahrami * 
 2, Abbas Afkhami3
2, Abbas Afkhami3 
 , Farshid Ghorbani Shahna4
, Farshid Ghorbani Shahna4 
 , Mohammad Javad Assari4
, Mohammad Javad Assari4 
 , Maryam Farhadian5
, Maryam Farhadian5 

1- Department of Occupational Health and Safety, School of Public Health, Behbahan Faculty of Medical Sciences, Behbahan, Iran
2- Center of Excellence for Occupational Health, Occupational Health and Safety Research Center, School of Public Health, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran ,Bahrami@umsha.ac.ir
3- Faculty of Chemistry, Bu-Ali Sina University, Hamadan, Iran
4- Center of Excellence for Occupational Health, Occupational Health and Safety Research Center, School of Public Health, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
5- f Medical Sciences, Hamedan, Iran
2- Center of Excellence for Occupational Health, Occupational Health and Safety Research Center, School of Public Health, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran ,
3- Faculty of Chemistry, Bu-Ali Sina University, Hamadan, Iran
4- Center of Excellence for Occupational Health, Occupational Health and Safety Research Center, School of Public Health, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
5- f Medical Sciences, Hamedan, Iran
Abstract: (559 Views)
Introduction: Toluene, benzene, xylene, and ethylbenzene (BTEX) belong to the class of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and are identified as toxic volatile compounds due to their harmful properties. The reliable biomarkers for occupational exposure to these toxic compounds are hippuric acid (HA), trans,trans-muconic acid (tt-MA), mandelic acid (MA), and methylhippuric acid (MHA), which correlate with toluene, benzene, ethylbenzene, and xylene, respectively.
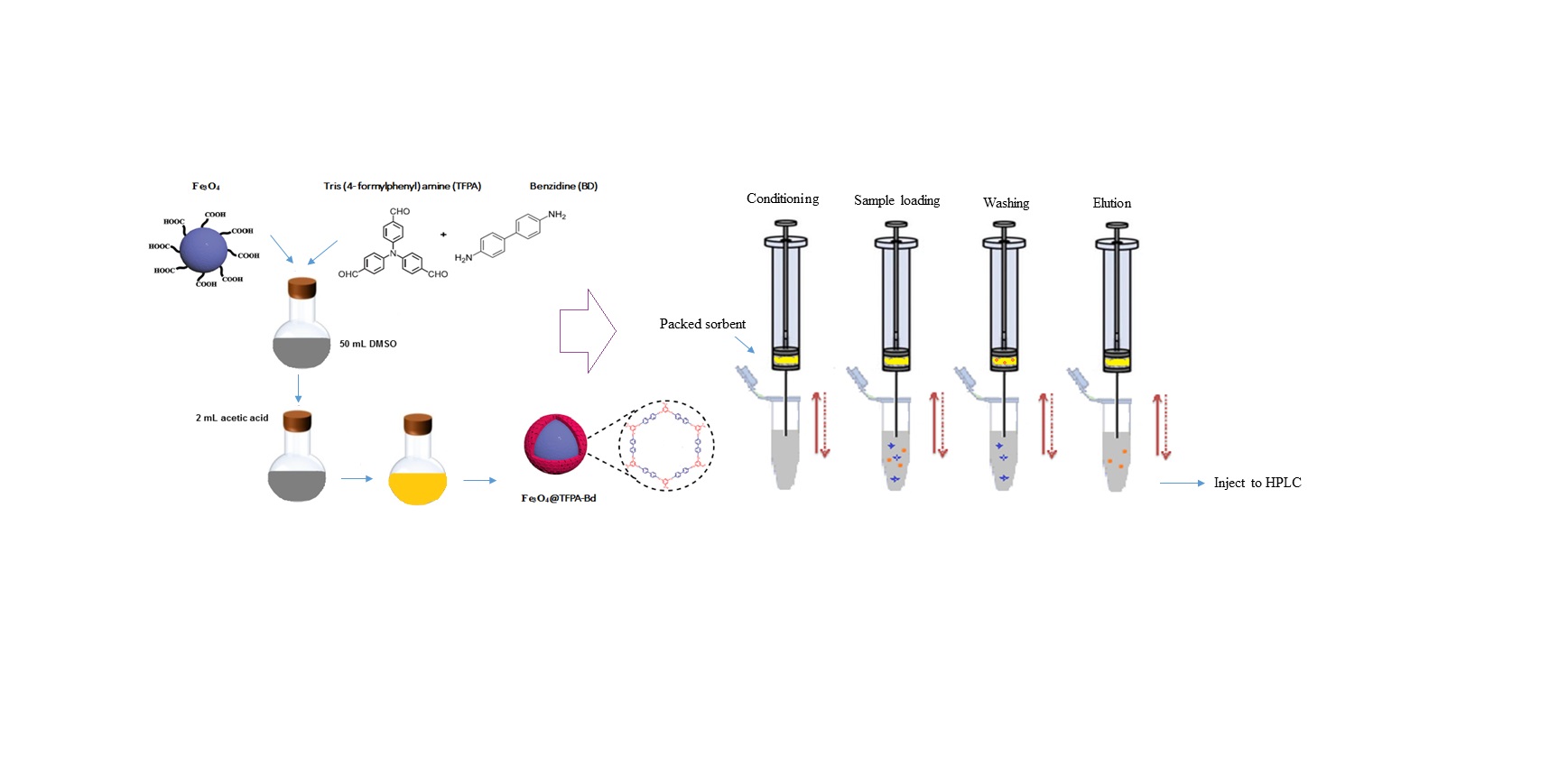
Material and Methods: A novel magnetized imine-linked covalent organic framework (Fe3O4@TFPA-Bd) was synthesized, marking its inaugural use as a sorbent in microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS). The synthesis of Fe3O4@TFPA-Bd was executed in a straightforward and efficient manner, using Fe3O4 nanoparticles as the magnetic core and benzidine (Bd) and Tris (4-formyl phenyl) amine (TFPA) as the structural building blocks. This newly produced sorbent was tested for the microextraction of hippuric acid (HA), mandelic acid (MA), trans, trans-muconic acid (tt-MA), and m-methyl hippuric acid (m-MHA) from urine samples, which were then analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). In order to optimize the extraction performance, parameters like sample volume, elution volume, extraction cycles, pH, and sample solution temperature were thoroughly adjusted. The synthesized adsorbent underwent thorough characterization via scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM), Fourier transforms infrared spectrometer (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
Results: The developed method showcased promising attributes: low detection limits (0.02 µg/ml for tt-MA, S/N=3), low quantification limits (0.06 µg/ml for tt-MA, S/N=10), a solid linear range (0.5-320 µg/ml for MA, R > 0.99), and commendable intra- and inter-day precision (2.4%-4.3% and 3.1%-7.8%, respectively) for volatile organic compound (VOC) biomarkers. Furthermore, the method demonstrated recoveries in the 81-87.5% range for spiked samples, indicating its practicality and effectiveness.
Conclusion: The developed procedure was suitable for the determination of BTEX biomarkers from urine samples and can be an alternative to previous methods.
Material and Methods: A novel magnetized imine-linked covalent organic framework (Fe3O4@TFPA-Bd) was synthesized, marking its inaugural use as a sorbent in microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS). The synthesis of Fe3O4@TFPA-Bd was executed in a straightforward and efficient manner, using Fe3O4 nanoparticles as the magnetic core and benzidine (Bd) and Tris (4-formyl phenyl) amine (TFPA) as the structural building blocks. This newly produced sorbent was tested for the microextraction of hippuric acid (HA), mandelic acid (MA), trans, trans-muconic acid (tt-MA), and m-methyl hippuric acid (m-MHA) from urine samples, which were then analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). In order to optimize the extraction performance, parameters like sample volume, elution volume, extraction cycles, pH, and sample solution temperature were thoroughly adjusted. The synthesized adsorbent underwent thorough characterization via scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM), Fourier transforms infrared spectrometer (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
Results: The developed method showcased promising attributes: low detection limits (0.02 µg/ml for tt-MA, S/N=3), low quantification limits (0.06 µg/ml for tt-MA, S/N=10), a solid linear range (0.5-320 µg/ml for MA, R > 0.99), and commendable intra- and inter-day precision (2.4%-4.3% and 3.1%-7.8%, respectively) for volatile organic compound (VOC) biomarkers. Furthermore, the method demonstrated recoveries in the 81-87.5% range for spiked samples, indicating its practicality and effectiveness.
Conclusion: The developed procedure was suitable for the determination of BTEX biomarkers from urine samples and can be an alternative to previous methods.
Keywords: BTEX biomarkers, Microextraction by packed sorbent, Covalent organic framework, HPLC-UV, Urine samples
Type of Study: Research |
Received: 2023/09/30 | Accepted: 2023/09/23 | Published: 2023/09/23
Received: 2023/09/30 | Accepted: 2023/09/23 | Published: 2023/09/23
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |